It seems that AI is all anyone in tech can talk about. But with so much hype, it can be difficult to separate fact from fiction. And when you can’t do that, marketing a product becomes difficult. A key part of understanding the current landscape is knowing the difference between common terms, such as generative AI vs machine learning.
When you understand the specific terms and what they mean, you can better determine how to market products by explaining how they solve real problems for your customers. Let’s start by exploring the distinctions between these two powerful technologies.
Hype bubble
Today, much of the marketing for AI is only talking about generative AI. This is one reason you need to understand the differences between generative AI vs Machine Learning.
Take a look at Google trends for the term “generative AI” since 2022, when generative models such as ChatGPT and DALL-E were introduced.
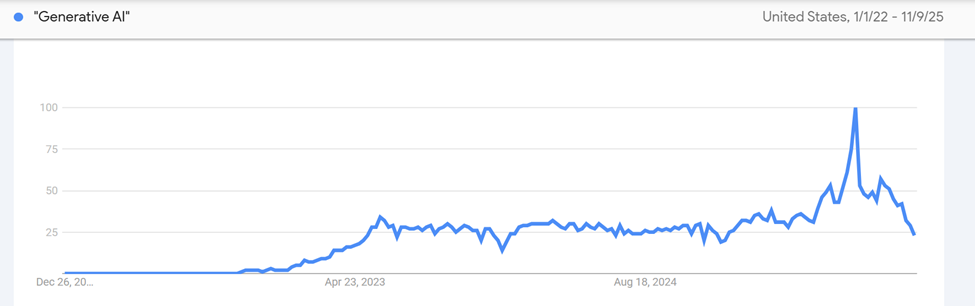
But the term “machine learning” has been a popular search since the beginning of Google in 2007.
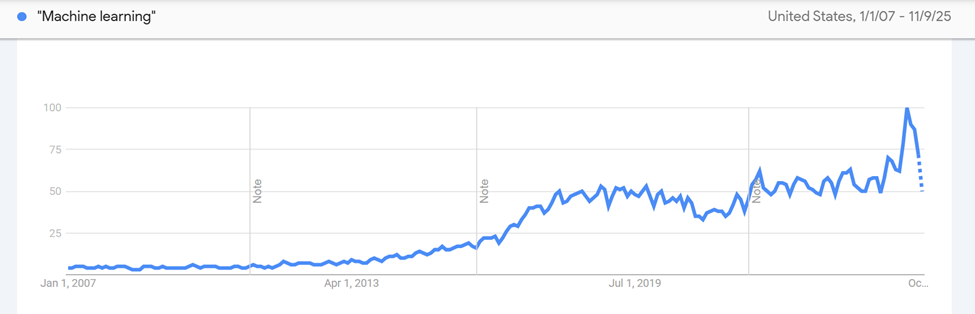
Here’s a comparison of the terms generative AI vs. machine learning since the end of 2021:
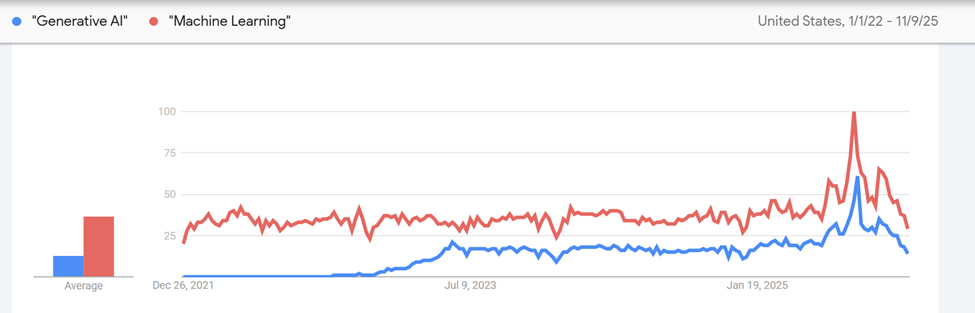
Google search trends show that historically, there is more interest in machine learning than generative AI. Why is that?
Definitions
Generative AI creates new content from existing data. Different models rely on vast amounts of data to generate text, images, music, and more, based on the way they have been trained with advanced algorithms.
According to IBM, this is the definition of Machine Learning:
a branch of AI focused on enabling computers and machines to imitate the way that humans learn, to perform tasks autonomously, and to improve their performance and accuracy through experience and exposure to more data.
Machine Learning (ML) is an entire subset of Artificial Intelligence. Algorithms are applied to large amounts of data so that the ML program can “perform tasks autonomously, and… improve their performance and accuracy through experience and exposure to more data” (via IBM). Machine learning is what fuels descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive AI applications.
Machine Learning Categories
There are three ways to perform machine learning. With supervised learning, the models are trained with labeled data sets. My colleague Tony Foster stepped through training a model to recognize cats in our VMworld session last year.
With unsupervised learning, the models use unlabeled data sets. This is what helps you find data trends you may not know to look for.
Reinforcement learning trains models “through trial and error to take the best action by establishing a reward system”. This could be as simple as letting the model know when it made the right decision.
Most Enterprise AI work is done by Machine Learning
Here’s a list of ML applications you probably already use (via TechTarget):
- Chatbots use ML and natural language processing (NLP) to mimic conversation.
- Digital assistants such as Siri and Alexa are powered by ML.
- Recommendation engines process your past purchases + current inventory + what other customers are buying to give you recommendations of what you should buy too.
- Dynamic pricing helps companies adjust the prices they charge based on market conditions. Controversially, it seems they have been marrying recommendation engines and dynamic pricing to charge different prices for individual consumers.
- Speech recognition can record calls, monitor customer calls with human agents, and provide language translation.
Generative AI depends on Machine Learning
Generative AI relies on machine learning techniques to work. It often uses NLP and computer vision in its creation process. Other ML disciplines Gen AI uses include (via Blue Prism):
- Large Language Models (LLMs) use statistical probabilities to figure out patterns in large sets of data. They use a process called self-supervised pre-training.
- Generative adversarial networks (GANs) are unsupervised learning techniques that pit two neural networks against each other during training.
- Transformers use math to identify the context and relationships between data.
- Diffusion generates new data.
This means it’s not generative AI vs machine learning, it’s really that machine learning is the foundation for generative AI.
Generative AI vs. Machine Learning: Moving beyond buzzwords to real solutions
Ultimately, generative AI and machine learning are powerful tools, but their true value lies in how they solve specific business challenges. That’s why it’s essential for organizations to define goals, evaluate needs, and choose the right approach to drive meaningful results.
Similarly, if you’re a vendor, cutting through the AI hype requires clear, value-driven messaging about your product. Throwing a buzzword into your copy won’t sway a potential customer who understands their needs, and which AI approach they want to take. Understanding the types of AI will help you create an accurate picture of what your product does.
To help you get started, we offer one-on-one “Ask Me Anything” (AMA) sessions to help you navigate the complexities of AI concepts and terminology. Building strong foundational knowledge will empower you to ask smarter questions and develop more impactful marketing strategies. To schedule a session for you or your team, drop a comment below or send us an email.
Key Points in the Article
- Understanding the AI Landscape: Differentiating between generative AI and machine learning is crucial for effective marketing and product positioning in the AI space.
- Current Trends and Public Interest: Google search trends show more sustained interest in machine learning over generative AI, highlighting the foundational role of ML in AI development.
- Definitions of Key Terms: Generative AI creates new content from data using models like LLMs and GANs, while machine learning involves algorithms that enable computers to learn and improve from data.
- Applications of Machine Learning in Business: Machine learning drives many enterprise AI applications such as chatbots, digital assistants, recommendation engines, dynamic pricing, and speech recognition.
- Relationship Between Generative AI and Machine Learning: Generative AI relies on machine learning techniques as its foundation, using disciplines like NLP and computer vision to generate new data.